Most of us only have experience in hospitals and operating rooms as the patient, and between the whirlwind of prep and our own nerves it’s all but impossible to remember the names of the dozen or so people littering the room, never mind why they’re there in the first place.
It turns out that the surgeons, nurses, anesthetists, et al have similar issues with remembering each others names and roles, as well, which can slow them down and even cost patients their lives in extreme situations.
The World Health Organization surgical safety checklist requires all staff to introduce themselves before surgery, but Dr. Hackett noticed that the section of the checklist was ticked without being completed – and even when it was, names and duties would go in one ear and out the other.
“When it’s done properly,” he says, “there are a few giggles from people, which tells me it’s not done regularly.”
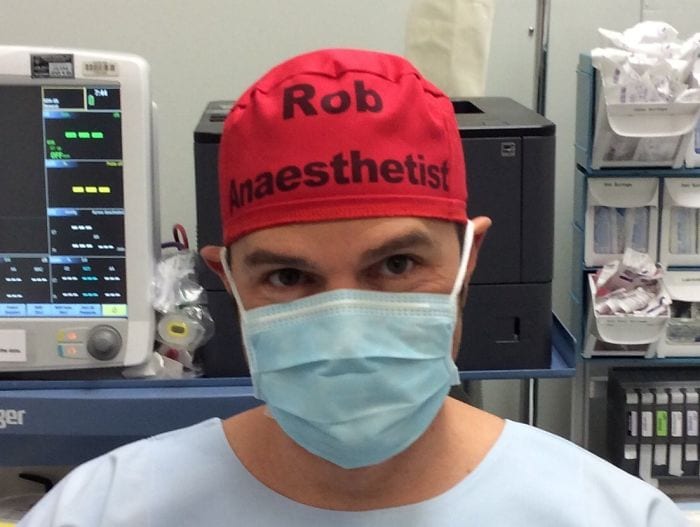
This is why Australian anesthetist Dr. Rob Hackett started wearing a scrub cap that said “Rob Anaesthetist” on it when entering an operating theatre. He challenged others to do the same through #TheatreCapChallenge, an initiative from the PatientSafe Network in response to concerns over how avoidable mistakes and poor communication can contribute to poor outcomes for patients.
Dr. Hackett says he’s faced pushback from some doctors but hopes that in the future a wider range of professionals will jump on board.
“There were some snide remarks, like ‘can’t you remember your name?’ …While there’s been support for name & role caps from anaesthetic and obstetric societies, it’s interesting to observe that we’re yet to receive any active support from a surgical college. Here’s a golden opportunity for them to face up to the bullying nature they’ve been tarred with.”
Even though the movement has room to grow, medical professionals from across the globe are showing their support by making their own caps and tweeting selfies using his hashtag #TheatreCapChallenge. Others agree with Dr. Hackett that knowing everyone’s name can save vital, life-and-death seconds in an operating room.
While it may sound crazy to think just having to repeat something or ask someone’s name, when seconds literally count, no positive change is too small.
“I went to a cardiac arrest in a theatre where there were about 20 people in the room,” Dr. Hackett recalls. “I struggled to even ask to be passed some gloves because the person I was pointing to thought I was pointing to the person behind them. It’s so much easier to coordinate when you know everyone’s names. It’s great for camaraderie and it’s great for patients as well.”
His movement is picking up steam and the data suggests there are benefits that reach beyond his original intent.
“UK studies have shown increased name recall amongst staff from 42 to 85%, increased name and role introductions during the surgical safety checklist from 38 to 90%. Simulation studies at Stanford University in the US demonstrated greatly increased communication and theatre efficiency.”
Women who have c-sections and are generally awake in an operating theatre also benefit from being able to address the people around them and have an awareness of why they’re there, as well.
An unintended benefit of writing on a scrub cap could also be people choosing to purchase re-usable caps as opposed to single-use ones – as of now, a 20-theatre hospital discards over 100,000 of them every year and spends about $10k of its annual budget on disposable caps. The material they’re made from is harmful to the environment and takes forever to break down, so there’s an environmental and financial upside to switching.
Hackett believes that being forced to admit that they’ve been hurting – even killing – patients for years can be one reason people struggle with accepting his simple fix for the problem.
“Cognitive dissonance is one of the challenges that #TheatreCapChallenge has faced. It’s most likely to affect those who feel defined by their decisions, often those further up the chain of command – in accepting change they’ll need to accept that what was happening previously, on their watch as it were, was not as good.”
Here’s hoping our healthcare providers – all of them – can check their egos at the door in order to forge a better, safer future for everyone who finds their lives in a hospital’s hands.
The post This Doc’s Decision to Write His Name on His Scrub Cap is Making Hospitals Everywhere Safer appeared first on UberFacts.