Making dry ice is easier than you thought! All you need is a pillow case, some gloves and a fire extinguisher. Watch below!
Phobias Might Be Memories Passed Down From Ancestors In Your DNA
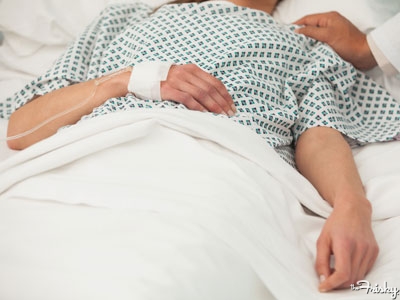
Memories may be passed down through generations in DNA in a process that may be the underlying cause of phobias.
Memories can be passed down to later generations through genetic switches that allow offspring to inherit the experience of their ancestors, according to new research that may explain how phobias can develop.
Scientists have long assumed that memories and learned experiences built up during a lifetime must be passed on by teaching later generations or through personal experience.
However, new research has shown that it is possible for some information to be inherited biologically through chemical changes that occur in DNA.
Researchers at the Emory University School of Medicine, in Atlanta, found that mice can pass on learned information about traumatic or stressful experiences – in this case a fear of the smell of cherry blossom – to subsequent generations.
The results may help to explain why people suffer from seemingly irrational phobias – it may be based on the inherited experiences of their ancestors.
So a fear of spiders may in fact be an inherited defence mechanism laid down in a families genes by an ancestors’ frightening encounter with an arachnid.
Dr Brian Dias, from the department of psychiatry at Emory University, said: “We have begun to explore an underappreciated influence on adult behaviour – ancestral experience before conception.
“From a translational perspective, our results allow us to appreciate how the experiences of a parent, before even conceiving offspring, markedly influence both structure and function in the nervous system of subsequent generations.
“Such a phenomenon may contribute to the etiology and potential intergenerational transmission of risk for neuropsychiatric disorders such as phobias, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder.”
See full articles from Telegraph
Making Electricity From Urine
Scientists have developed a way to convert urine in to a renewable energy source. But as Sally Magnusson, author of Life of Pee and presenter of Radio 4’s Secret Science of Pee, writes in this viewpoint feature, there is some way to go before the idea is embraced more widely.
A growing number of scientists have cottoned on to the fact that urine is a source of vital enzymes for medicine, precious minerals like fast-depleting phosphorus, and chemical compounds like urea, which are crucial to the manufacture of fertilisers, plastics and cosmetics and can also be used to make electricity.
The question is, can urine help us? And if so, can we see it not as a useless, embarrassing waste product, but as a substance that could drive the next stage of the green revolution?
I started out mildly intrigued by the range of uses urine had in centuries gone by – it was used in the manufacture of gunpowder, alum, dyes, paint and stained glass, to clean Roman togas, and heal wounds.
I wrestled with the revulsion that arises when we move from historical curiosity to envisaging personal application, but I ended up convinced there is an urgent role for urine again in the 21st Century, based on its unique scientific properties.
Urea, an important constituent of urine, is the key to many modern applications.
At Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, the Youtricity research team has developed a urine-powered system to generate electricity.
The carbamide power system runs on urea fuel cells sourced from human urine.
Dr Shanwen Tao, who invented the technology, said urea fuel cells were similar to hydrogen fuel cells, but used urea instead.
His colleague, Dr Robert Goodfellow said it had been a “huge” breakthrough in the search for renewable energy, but the system was being further developed.
See the full article from BBC News
Spending Money On Others Makes You Happier
In their book Happy Money: The Science of Smarter Spending, authors Elizabeth Dunn and Michael Norton draw on years of quantitative and qualitative research to explain how money can buy happiness, but only if we spend it in certain ways.
The key lies in adhering to five key principles: Buy Experiences (research shows that material purchases are less satisfying than vacations or concerts);Make it a Treat (limiting access to our favorite things will make us keep appreciating them); Buy Time (focusing on time over money yields wiser purchases); Pay Now, Consume Later (delayed consumption leads to increased enjoyment); and Invest in Others (spending money on other people makes us happier than spending it on ourselves).
Recently we featured a video illustrating the emotional benefits of buying experiences. In the following sequel, Norton again gives some cash to two women in Harvard Square. The catch this time: Each of them must spend the money on someone else.
“We’ve shown in our research that giving money to others actually does make people happier,” says Norton, an associate professor of marketing at Harvard Business School. “One of the reasons is that it creates social connections. If you have a nice car and a big house on an island by yourself, you’re not going to be happy because we need people to be happy. But by giving to another person, you’re…creating a connection and a conversation with that person, and those things are really good for happiness.”
Watch the video to find out how the women in Harvard Square chose to invest in others—and whether it made them happier!
Full Article from Forbes.com
Eating Chocolate Can Improve Math Skills
 Eating chocolate could improve the brain’s ability to do math, a new study suggests.
Eating chocolate could improve the brain’s ability to do math, a new study suggests.
Mental arithmetic became easier after volunteers had been given large amounts of compounds found in chocolate, called flavanols, in a hot cocoa drink.
They were also less likely to feel tired or mentally drained, the findings, presented at the British Psychological Society annual conference in Brighton show.
Prof David Kennedy, director of the brain, performance and nutrition research centre at Northumbria University, and a co-author of the study, said that chocolate could be beneficial for mentally challenging tasks.
The findings suggest students who binge on chocolate when revising for exams may gain a real benefit from doing so.
“For things that are difficult to do, mentally demanding things that maybe crop up in your work it could help,” Prof Kennedy said.
The flavanols, part of a group of chemicals called polyphenols, work by increasing the flow of blood into the brain.
For the study 30 volunteers were asked to count backwards in groups of three from a random number between 800 and 999 generated by a computer.
The findings show that they could do the calculations more quickly and more accurately after they had been given the drink.
However, the same was not true when the group was asked to count backwards in groups of seven, which the researchers described as a more complex task, requiring a slightly different part of the brain.
The findings also show that the volunteers did not get as tired doing the calculations if they had been given the cocoa drink, despite being asked to do them over and over for an hour.
The researchers gave the volunteers a total of 500mg of flavanol.
Although the amount was too great to be found naturally in the diet, researchers said that people should ensure that they have lots of flavanols, also found in fruit and vegetables, on a regular basis.
Emma Wightman, one of the study’s lead researchers, said: “You can get bars of chocolate that have 100mg of flavanol, and we are also going to look at the effect of lower doses of flavanol on the brain.”
Dark chocolate contains higher quantaties of the chemical than plain or milk chocolate.
Prof Kennedy added: “The amount that you are giving is more than in the diet but there is quite a lot of evidence that general amounts are protective against declining function and that kind of thing.
“The more fruit and vegetables and things that are high in polyphenols the better that is for your brain in the long run.”
(via Telegraph)
66-Year-Old Man Discovers He’s A Woman!
A 66-year-old who lived his whole life as a man was given a surprising diagnosis after visiting the doctor in Hong Kong with a swollen abdomen — he was a woman.
Doctors realised the patient was female after they found the swelling came from a large cyst on an ovary, the Hong Kong Medical Journal reported.
The condition was the result of two rare genetic disorders.
The subject had Turner syndrome, which affects girls and women and results from a problem with the chromosomes, with characteristics including infertility and short stature.
But he also had congenital adrenal hyperplasia, increasing male hormones and making the patient, who had a beard and a “micropenis”, appear like a man.
“Were it not due to the huge ovarian cyst, his intriguing medical condition might never have been exposed,” seven doctors from two of the city’s hospitals wrote in the study published Monday.
Left Is Right And Right Is Left – The Human Brain Crossover
In the human brain, the left side actually controls the movement of the right side of the body, and the right side of the brain controls the movements of the left side of the body. Although in many ways both sides of the human brain are equal in the way they work, each side however
The post Left Is Right And Right Is Left – The Human Brain Crossover appeared first on Interesting Facts, Fun Facts and Weird Facts!.
Heroin was Actually a Brand Name!
When you buy a drink from your local shop you are overwhelmed with choice and brands. You can buy a can of 7UP, a bottle of Fanta or choose to drink Dr. Pepper, these are all recognisable names used to sell a product. However it may surprise you to find out that Heroin was once
The post Heroin was Actually a Brand Name! appeared first on Interesting Facts, Fun Facts and Weird Facts!.
Why is the sky blue?
Many people often wonder why the sky is blue and not another colour. Have you ever questioned yourself about this? Even though the sun’s light may look white/yellow it’s actually made up from all the colours of the rainbow. Throughout your life you would have seen the colour prism, that’s what happens with the light
The post Why is the sky blue? appeared first on Interesting Facts, Fun Facts and Weird Facts!.
Psychologists say a crush only lasts for 4 months. But when feelings last longer, you are considered to be “In Love”.
According to psychologists, a crush lasts on average for four months, if feelings persist beyond that, one is considered to be “in love”.
The post Psychologists say a crush only lasts for 4 months. But when feelings last longer, you are considered to be “In Love”. appeared first on Interesting Facts, Fun Facts and Weird Facts!.