The man credited with saving both Apollo 12 and Apollo 13 was forced to resign years later while serving as the Chief of NASA when Texas Senator Robert Krueger blamed him for $500 million of overspending on Space Station Freedom, which later evolved into the International Space Station (ISS).
Some of the Best Photos NASA’s Curiosity Rover Has Taken in Its 8 Years on Mars
NASA’s Curiosity landed on Mars on August 6, 2012 – if you remember, you could even sort of livestream its Martian landing. It became the only functional robot on the planet after NASA’s Opportunity stopped communicating on February 13, 2019.
After nearly 8 years of service, the Curiosity has taken some amazing pictures of the Red Planet (and it’s still trundling around doing it’s thing). You can check out the thousands of images on NASA’s official website.
In the meantime, here’s a quick preview of the beauty of Mars.
15. Curiosity Selfie!
Even robots want to take a picture now and then.
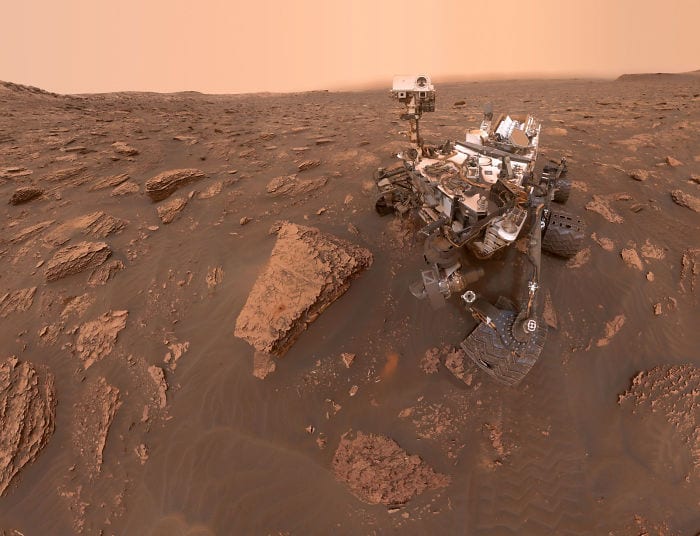
Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
14. A Petrified Area
These patterns are just beautiful.
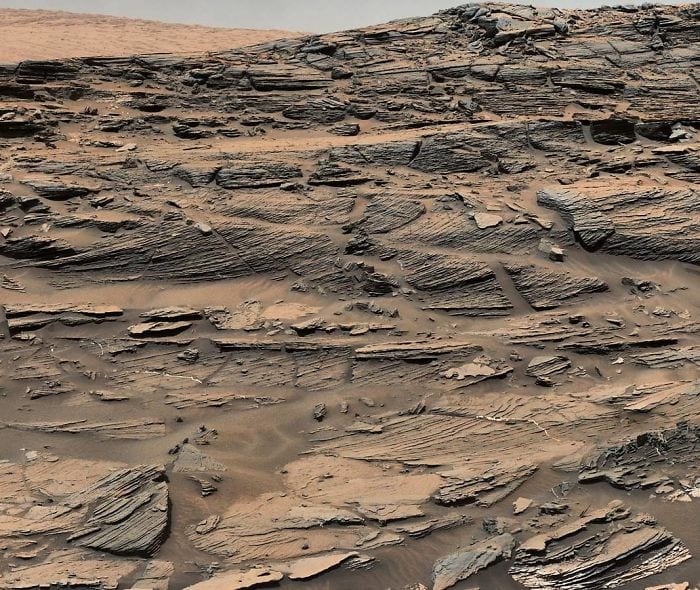

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
13. Check out These Gorgeous Views
Worthy of a museum exhibit!

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
12. Checking out Its Own Wheel Track
It’s a meta portrait.
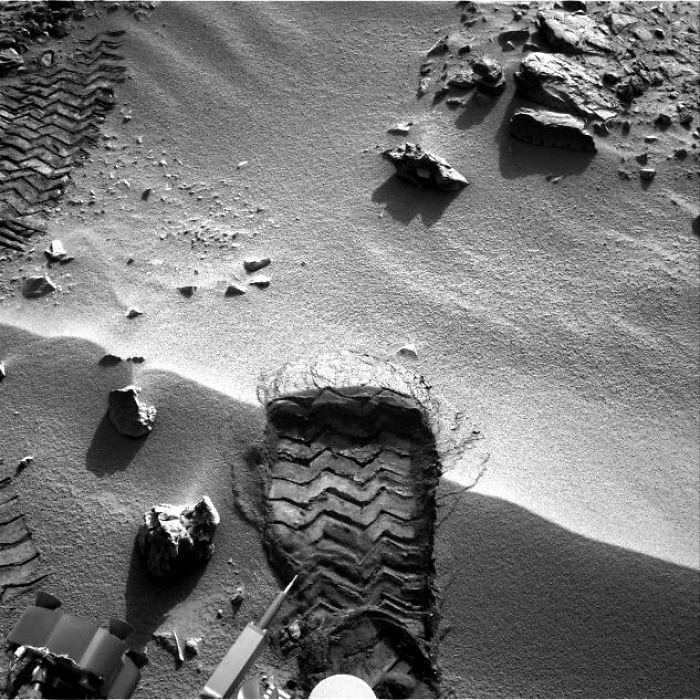

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
11. An Active Sand Dune
Called Gobabeb, this sand dune belongs to a dune field called Bagnold.
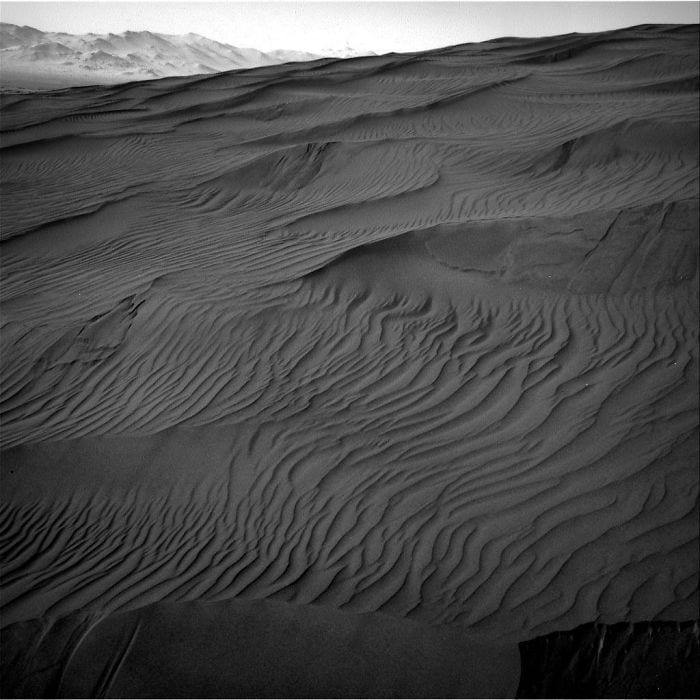

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
10. Mount Sharp’s Base
This is mudstone.
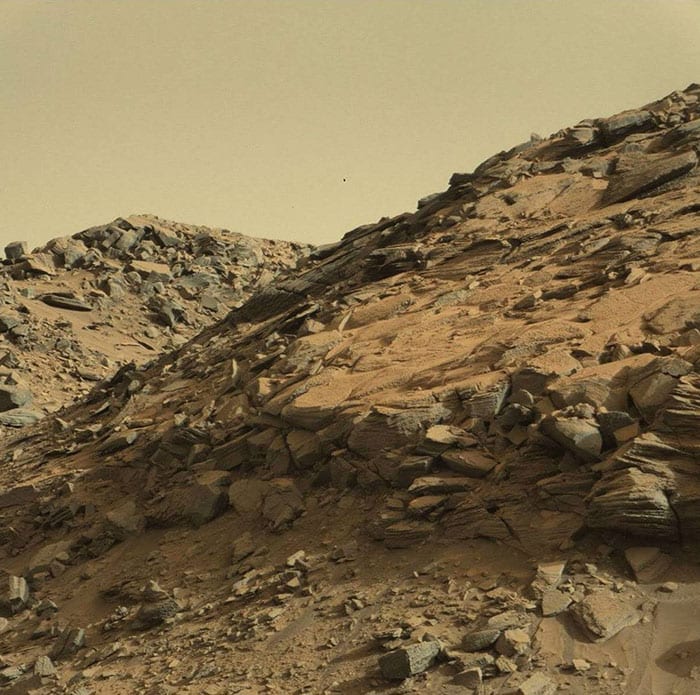

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
9. Yet Another Shot of Mount Sharp
These sedimentary rocks are still charming to look at.
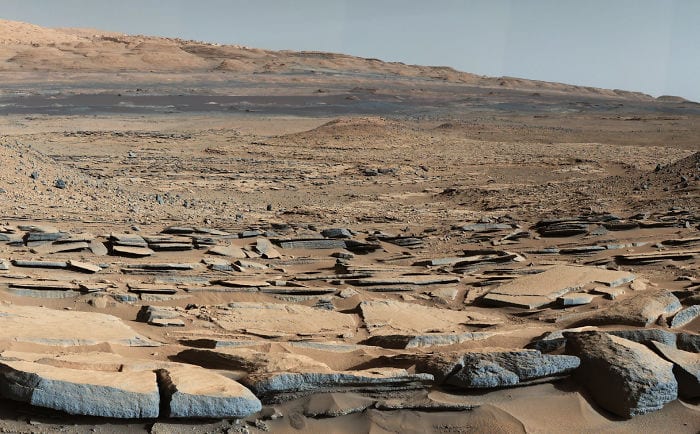

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
8. A Wide Shot
Actually taken from a Mars Orbiter, not by Curiosity.
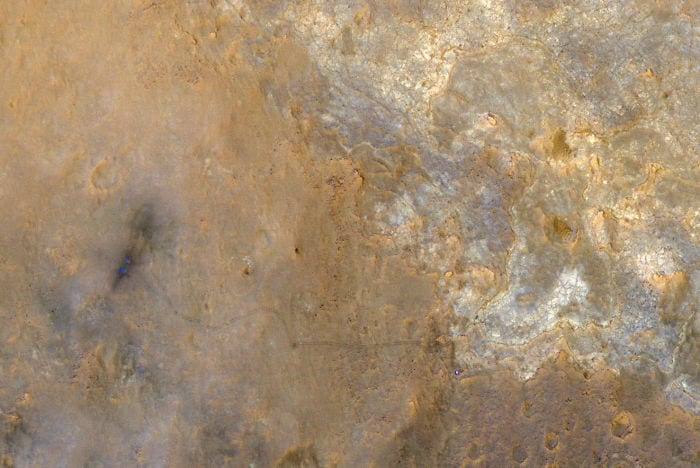

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
7. Fracture Shot
This has many rocks that look as if they’ve been, well, fractured.
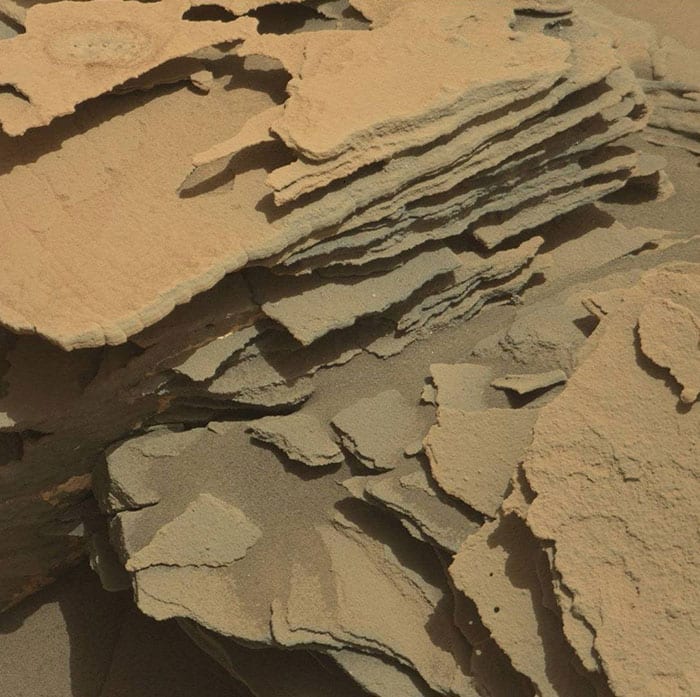

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
6. A Rocky Dreamscape
It looks like a dream!
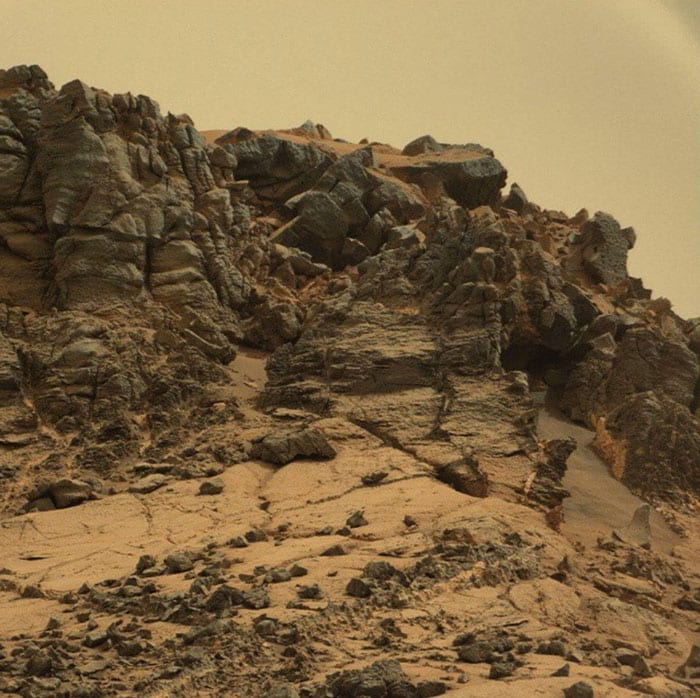

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
5. Wide-Shot of Mount Sharp
This far-off view definitely speaks for itself!
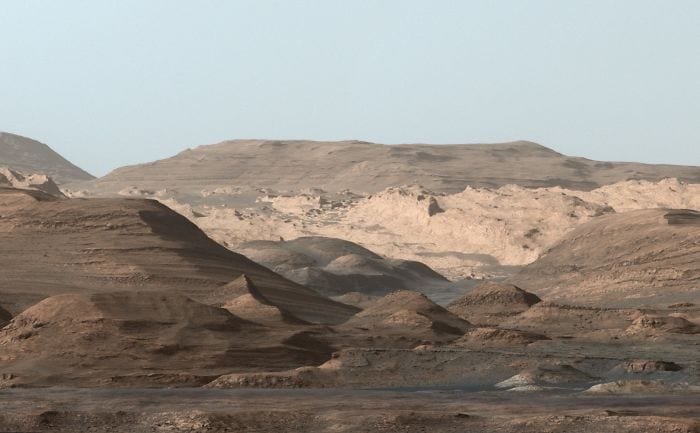

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
4. The Bottom of Mount Sharp
There are many great angles of this mountain.
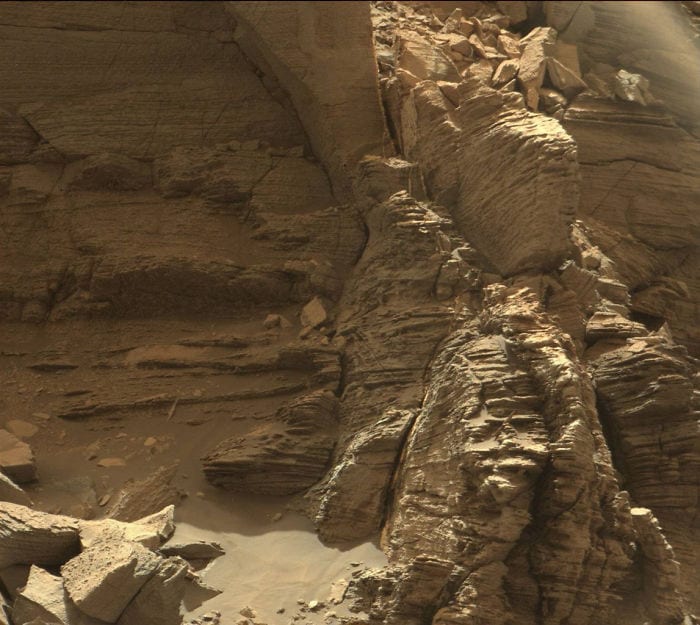

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
3. Take a Gander at This!
It’s called Jake Matijevic Rock.
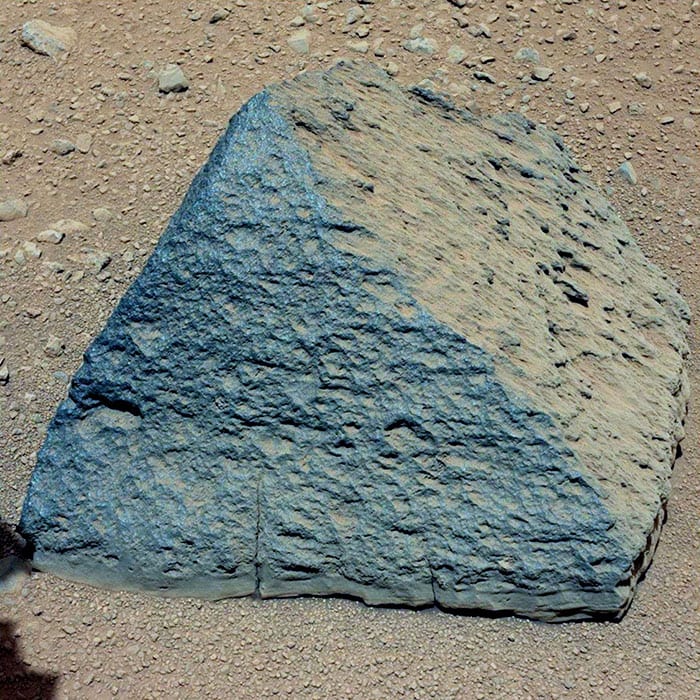

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
2. The “Harrison” Rock
There are some crystals in this shot too!
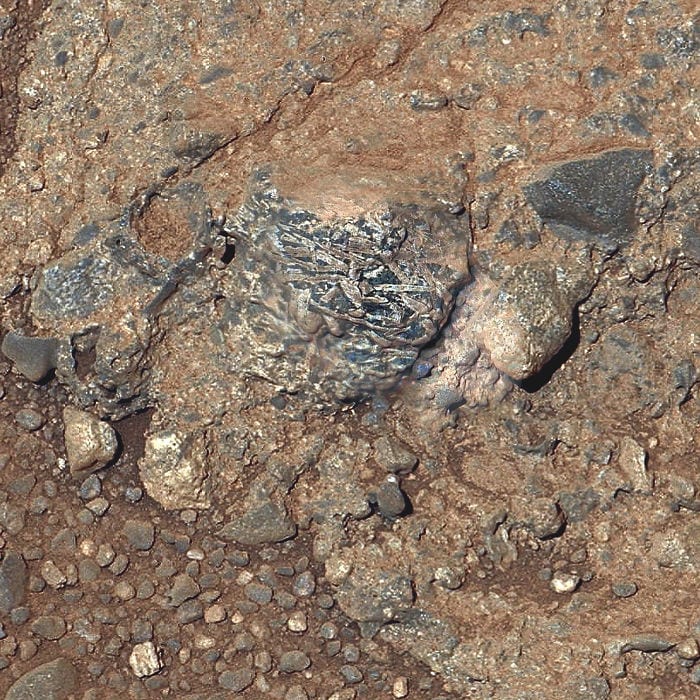

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
1. Martian Sunset
If it looks other-worldly, that’s because it is!

Photo Credit: NASA Mars Exploration Program
As of now, the Curiosity is still doing strong on Mars.
If you’ve got thoughts, we totally look forward to hearing anything you have to say about these landscapes. All scientific facts, discussion, and theories are totally welcome in the comments.
The post Some of the Best Photos NASA’s Curiosity Rover Has Taken in Its 8 Years on Mars appeared first on UberFacts.
Wow! Astronomers Watched a Star Skip the Supernova Stage and Go Straight to Black Hole.
When people say “go out with a bang”, they usually don’t mean literally. But when it comes to dying stars, typically astronomers expect them to go out with enormous bangs: supernovae. However, recently a group of Ohio University scientists observed a star that didn’t have quite the same life path in mind.
Instead of exploding and then collapsing in on itself, the star turned directly into a black hole. That shocked the group of scientists who had been studying the star, named N6946-BH1 to be exact, which was located in the Fireworks Galaxy, 22 million light-years away. At first they didn’t think it was possible, yet in 2015, after six years of watching the star weaken, scientists concluded that the star had bizarrely skipped the supernova stage.
They chalked it up as a “massive fail.” That’s a technical term, referring to the star’s mass.
“The typical view is that a star can form a black hole only after it goes supernova,” said Ohio State astronomy professor and study researcher Christopher Kochanek. “If a star can fall short of a supernova and still make a black hole, that would help explain why we don’t see supernovae from the most massive stars.”
Photo Credit: Pexels
This atypical event still requires more analysis, but scientist Scott Adams estimates that massive fails occur in about 10 to 30 percent of massive stars. Ultimately, this discovery could lead to more answers about how super-massive black holes come to exist, since supernovae tend to blow away a lot of a star’s mass.
Without a supernova, more of a star’s mass would stick around to collapse in on itself and become a vortex that bends time and space and eats light for supper.
The post Wow! Astronomers Watched a Star Skip the Supernova Stage and Go Straight to Black Hole. appeared first on UberFacts.
A Teenager Discovered a Planet on the Third Day of His NASA Internship
These kids today…are pretty great, as it turns out!
At least, some of them are.
On only the third day into his internship at NASA, a 17-year-old named Wolf Cukier (awesome name) discovered a new planet that is being called “TOI 1338 b”. The planet is 6.9 times larger than Earth, and the folks at NASA believe the planet will be in a stable orbit for at least the next 10 million years. It is located roughly 1,300 light-years away from Earth.
View this post on Instagram
The teenager discovered the planet while looking at “variations in star brightness” in images captured by NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).
Cukier is from Scarsdale, New York, and he completed a two-month internship last summer with NASA at their Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland.
17-year-old high school student discovers rare new planet 3 days into NASA internship https://t.co/cUlDKsHgeU pic.twitter.com/ujR6H3hYBR
— CBS News (@CBSNews) January 11, 2020
Cukier said, “I was looking through the data for everything the volunteers had flagged as an eclipsing binary, a system where two stars circle around each other and from our view eclipse each other every orbit. About three days into my internship, I saw a signal from a system called TOI 1338. At first I thought it was a stellar eclipse, but the timing was wrong. It turned out to be a planet.”
NASA just recently confirmed Cukier’s findings, and they submitted a paper co-written by the teenager about the discovery of the new planet.
Let’s get to meet this whiz kid, shall we?
Cukier also confirmed that he is indeed now looking for other new planets. Keep up the great work!
As the saying goes, the kids are alright.
The post A Teenager Discovered a Planet on the Third Day of His NASA Internship appeared first on UberFacts.
The Skylab “stowaway” prank
On September 10, 1973, NASA Astronaut Owen Garriott successfully pranked flight controllers by playing a recording of his wife whilst on SkyLab. There were no women on board the space station and was used to make it look like there was a stowaway. Controllers in Houston were startled to hear a woman’s voice beaming down […]
The Curiosity Rover Found Oxygen Behavior on Mars That Is Baffling Scientists
The Curiosity rover has been in Mars’ Gale Crater in 2012, and since then, has been studying all things Martian, so we can know more about the planet’s past.
Well, what we now know, more than anything, is how much we don’t understand about what’s happening out there.
Case in point: the rover’s tunable laser spectrometer (or Sample Analysis at Mars, SAM) recently found a huge amount of methane–the largest since landing there.

Photo Credit: NASA
Followed closely by the discovery that oxygen is behaving in a way scientists don’t quite understand.
In the past six years, SAM has determined the following about the atmosphere of Mars: 95 percent is carbon dioxide, 2.6 percent molecular nitrogen, 1.9 percent argon, 0.16 percent oxygen and 0.06 percent carbon monoxide.
Mars has seasons sort of like Earth, but they happen because the air pressure changes when carbon dioxide gas freezes at the poles during winter. This event causes the air pressure to lower. When the carbon dioxide eventually evaporates and is redistributed into the atmosphere, the air pressure rises for a Mars spring and summer.

Photo Credit: NASA
Nitrogen and argon followed a similar pattern.
Oxygen, however, didn’t.
It actually rose and peaked at 30 percent during spring and summer, then lowered to normal levels in fall.

Photo Credit: NASA
This pattern has repeated itself since Curiosity started monitoring. The only difference was that the levels of oxygen rising and falling varied.
Is the oxygen being created by something? What’s causing it to fall?
According to CNN, one of the authors of a new paper covering the seasonal variations, Sushil Atreya, said the data was “mind boggling.”
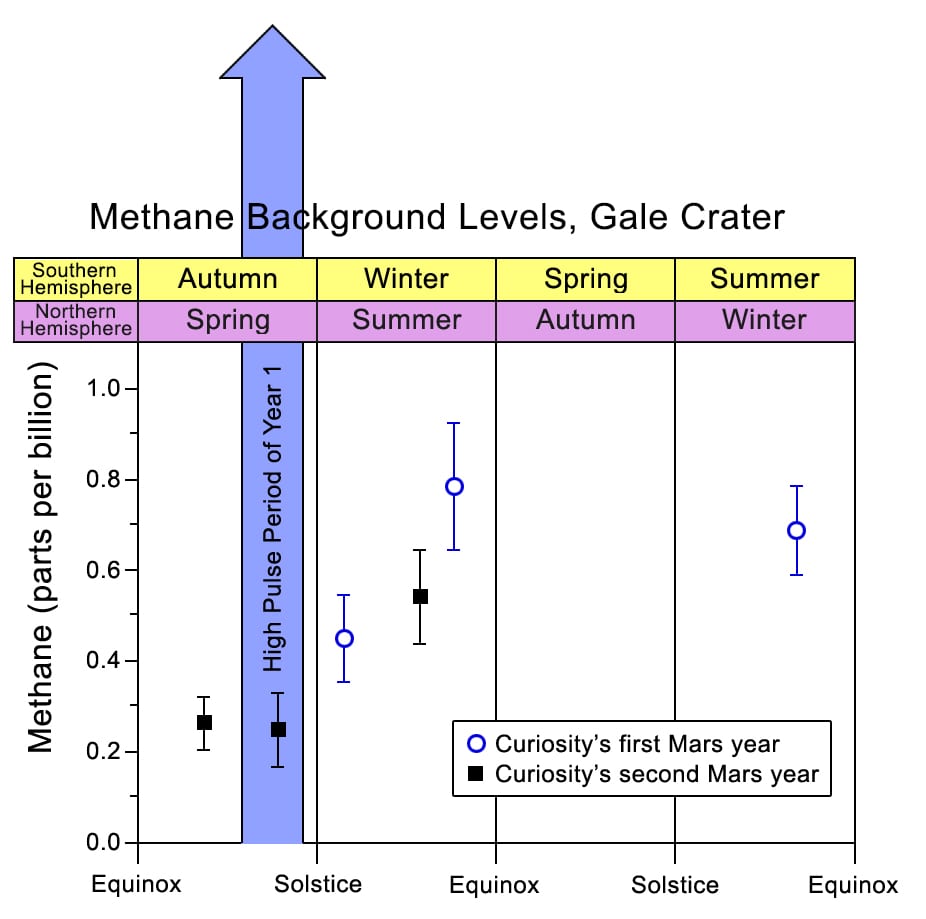
Photo Credit: NASA
The scientists involved in the study were so puzzled they even had the rover checked out for operational issues. But Curiosity was working as usual.
Melissa Trainer, study author and planetary scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, said:
We’re struggling to explain this. The fact that the oxygen behavior isn’t perfectly repeatable every season makes us think that it’s not an issue that has to do with atmospheric dynamics. It has to be some chemical source and sink (of elements into the soil) that we can’t yet account for.
So, what about the huge amount of methane?
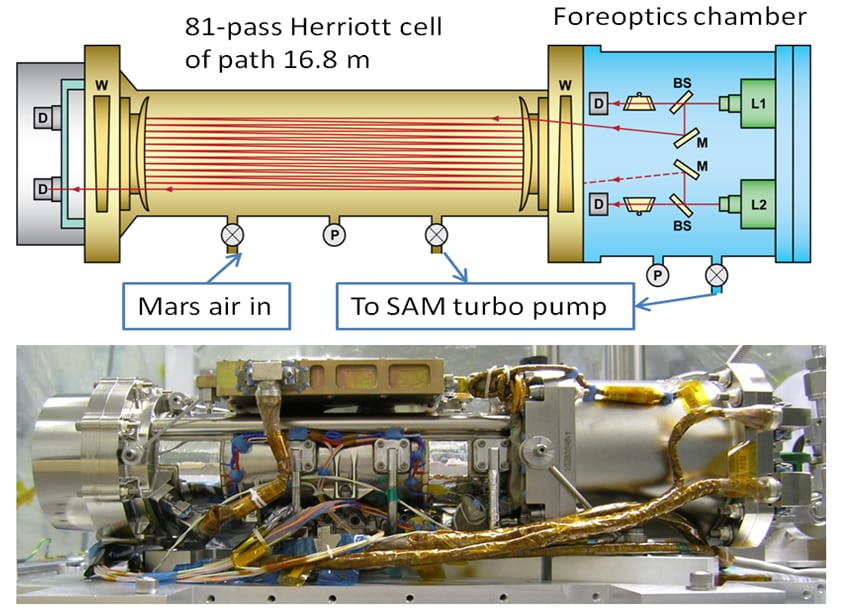
The Tunable Laser Spectrometer on NASA’s Curiosity Mars Rover
Photo Credit: NASA
On Earth, most of our methane is created by living things, but also by rocks and water. Mars has plenty of rocks and water.
Principal Investigator Paul Mahaffy of NASA’s Goddard Spaceflight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, noted that current measurement systems cannot determine the exact source of methane. What they do know, however, is that the methane fluctuates with the seasons as widely as oxygen.
Could the strange behavior of the two gases be related somehow?
Atreya believes so, although no one can figure out how.
In the meantime, the team invites any and all Martian experts to chime in.
The post The Curiosity Rover Found Oxygen Behavior on Mars That Is Baffling Scientists appeared first on UberFacts.
On December 16, 1965, NASA received…
On December 16, 1965, NASA received a prank transmission from two astronauts: “We have an object, probably in polar orbit… I see a command Module and and eight smaller modules in front. The pilot of the command module is wearing a red suit.” They then started playing, “Jingle Bells”.
Why Is the Sun Hot If Space Is so Cold?
The solar system is pretty extreme as far as temperatures go. At its core, our sun registers at around 27-million degrees Fahrenheit, but its surface is no slouch temperature-wise either: it’s clocks in at about 10,000 degrees.
So is it kind of weird that in outer space, away from the sun and the mild atmosphere of Earth, the temperature measures -455 degrees?
What’s really going on out there?
Let’s go over some basic physics. Heat is actually energy, radiating as an infrared wave (like light, but below the spectrum of what’s visible to human eyes) that moves from its source (ie, the sun) to…everything else. As infrared radiation comes into contact with molecules, it imparts some of its energy, causing them to become excited and heat up. But only the matter in the path of the radiation will heat up –any matter outside of the path will remain cold. Any void the energy travels through will also remain cold because there’s nothing in it to get warmer.
Consider the planet Mercury. As the planet turns and night falls, the newly dark surface plunges in temperature to 1000 degrees colder than the radiation-exposed day side.

Photo Credit: NASA
Earth, in contrast, feels warm even if you’re standing in the shade. Summer nights stay warm too. Even night during the wintertime in Canada is warmer than most other places in our solar system at night (withe some exceptions, notably Venus). This is due to the sun’s radiation causing convection and conduction.
When radiation hits molecules, the molecules pass that energy to others next to them, which then pass their extra energy on to their neighbors. This chain reaction is conduction. Areas outside of the path of radiation are warmed this way – so night stays warm (relatively speaking).
But in empty space there are fewer molecules that are too far apart to transfer energy if they are heated. Conduction, under these circumstances, can’t happen. This is the void issue we touched on earlier.
Convection, the process by which heat moves via a fluid (ie air or water), also can’t happen in low-gravity, molecule-scarce space.
Engineers at NASA takes all this in consideration when they are designing spacecraft for exploration. Out in space, probes and other equipment are exposed to temperatures either boiling hot or icy cold, depending on where they’re traveling in relation to the path of the sun’s radiation.
The closest any spacecraft has gotten to the sun was the Parker Solar Probe, which came within 15 million miles. This was only possible because of the specially designed heat shield that kept the rest of the probe cool.
Photo Credit: NASA
The ability to adjust to the rising and dropping in temperatures to the tune of hundreds of degrees Fahrenheit is a necessity for surviving the extremes of space.
Luckily, our balmy little home planet manages it for us surprisingly well.
The post Why Is the Sun Hot If Space Is so Cold? appeared first on UberFacts.
NASA Wants to Send a Probe to Venus’ Infernal Surface
Even though we’ve had our eyes on the Mars prize for some time, a different team of researchers is actually working on getting to Venus.
Venus gets closer to Earth in its orbit than any other planet, yet we have precious little information about the surface – except that it’s close to a living hell.
In 1966, a Soviet space probe crash-landed on the surface, where it lasted a few hours before being destroyed. Now NASA’s Long-Lived In-situ Solar System Explorer, or LLISSE, is looking to last a full 60 days in the reactive atmosphere, crushing pressure and blasting heat found on Venus’ surface. In fact, each probe has to be specially designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressure.
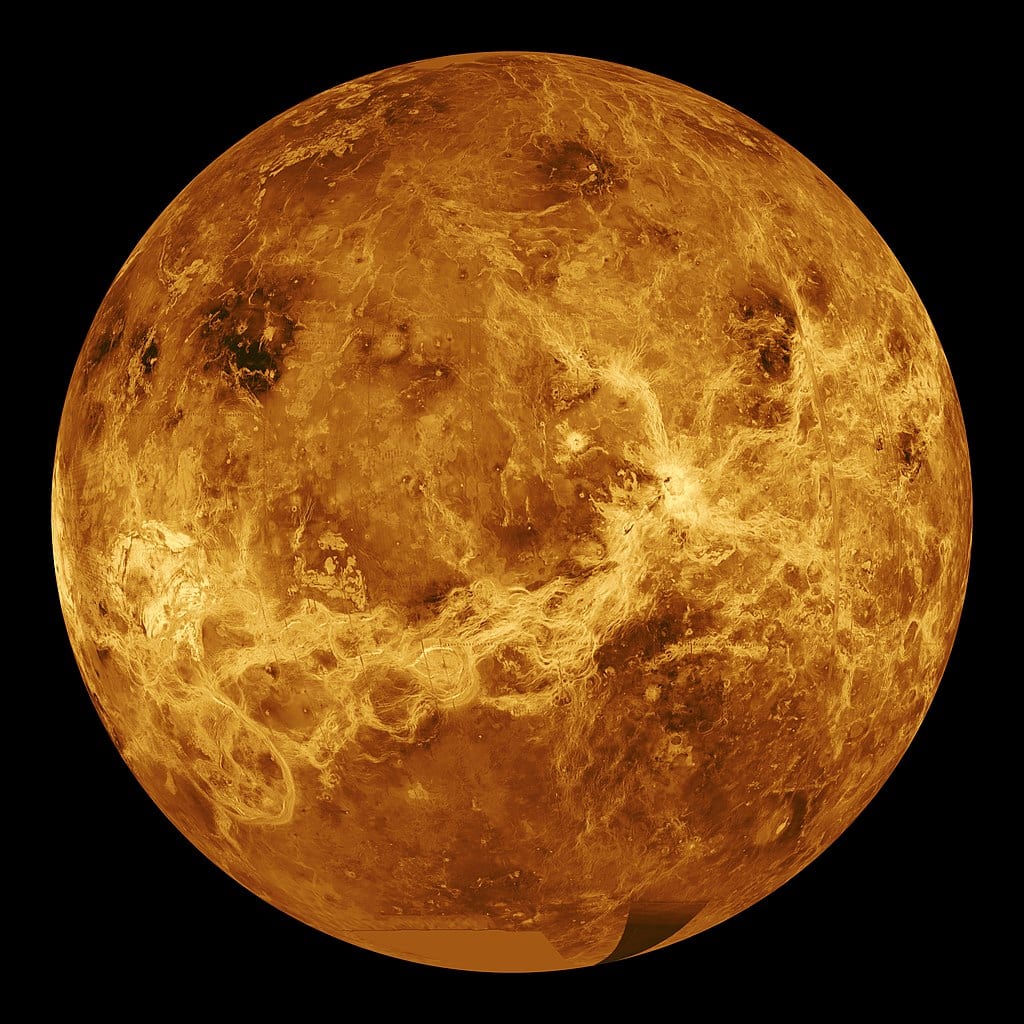

Photo Credit: Wikipedia
Called Earth’s evil twin, Venus is roughly the same size and mass of our home planet. Scientists say it was once water-rich, potentially with the elements necessary for life. But it has since turned into a hell planet with scorching, lead-melting temperatures, pressure comparable to what’s found at the bottom of our deepest oceans and winds whipping like tornados. During the day, sulphuric acid blocks the sun’s rays. The nights each last one hundred Earth-days.
One theory about what happened to make Venus so inhospitable is that, over time, the once huge, shallow ocean evaporated, releasing the super-light hydrogen atoms into space. As hydrogen disappeared, all the carbon-dioxide left in the atmosphere created an out-of-control greenhouse effect. Basically, turbo-charged climate change run utterly amok.
But we really don’t know.
And we can’t know, until we put some equipment on the surface.
Small as a ten-inch cube, LLISSE will piggyback on other space-going craft and then get dropped onto Venus. The unit is made of super hard silicon carbide – also used in sandpaper and lab-made diamonds – to protect it against sulphuric crystals. Like a missile, it will be powered by a heat-activated thermal battery for its 60-day life.
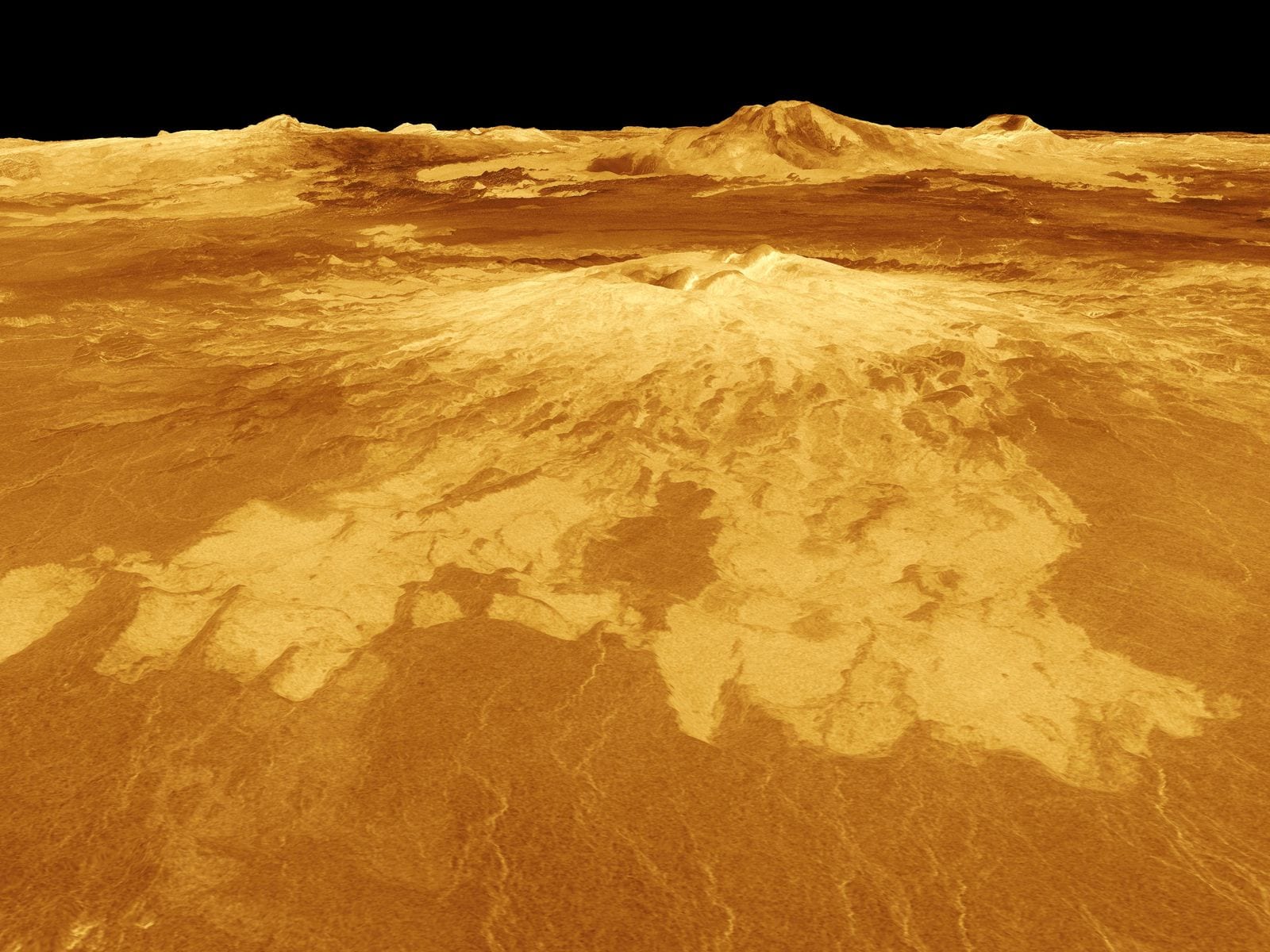
Photo Credit: NASA
NASA engineers need the unit powered for that long to see the change from day to night on Venus. Each Venus day lasts almost four Earth-months. If the unit can get placed late in the day, and if it can stay powered long enough, we’ll be get critical data on the transition for the first time.
Eventually, LLISSE will be used as part of a joint Venus project with the Russian space agency, but, as of right now, it looks as if nothing is getting to the next planet over before 2026. Frankly, it’s not even sure if LLISSE will ever get a trip into space at that point.
But the technology is already here, and Venus isn’t going anywhere.
A visit next door is just a matter of a few more Venus days.
The post NASA Wants to Send a Probe to Venus’ Infernal Surface appeared first on UberFacts.
15 Amazing Photos of What Mars Looks Like
It’s just like in Total Recall! Kind of…
The Curiosity Rover on Mars sends photos back from the red planet daily. And they are MINDBLOWING.
We, and NASA of course, still have so much to learn about Mars, but even these images would have been inconceivable not so many years ago.
Take a look at these stunning photographs.
1. Check that out
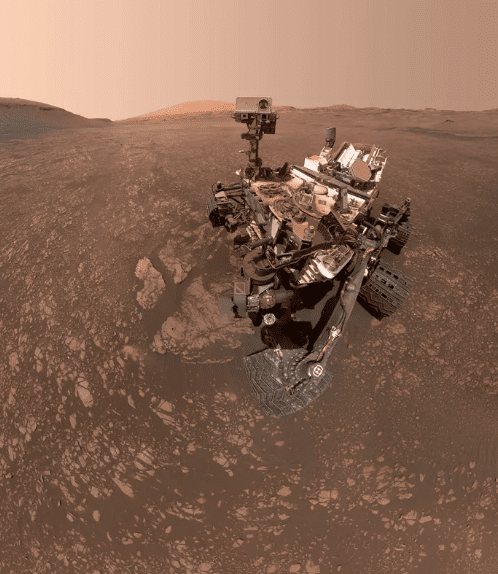
Photo Credit: NASA
2. Tracks
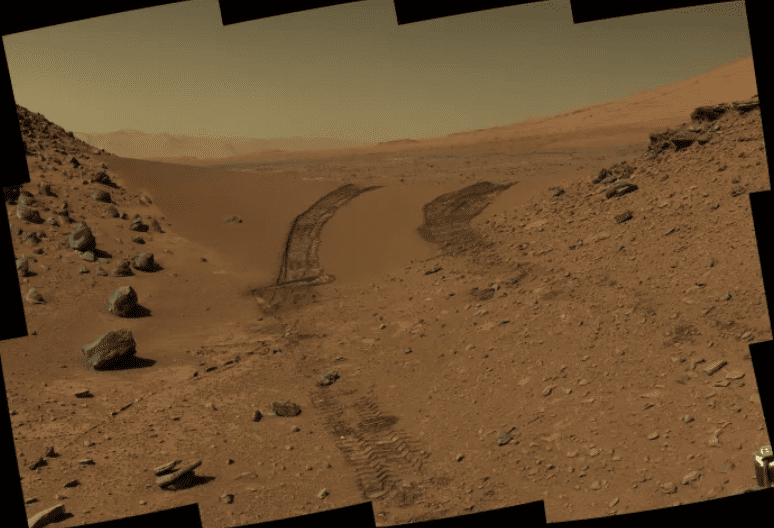

Photo Credit: NASA
3. On top of the world
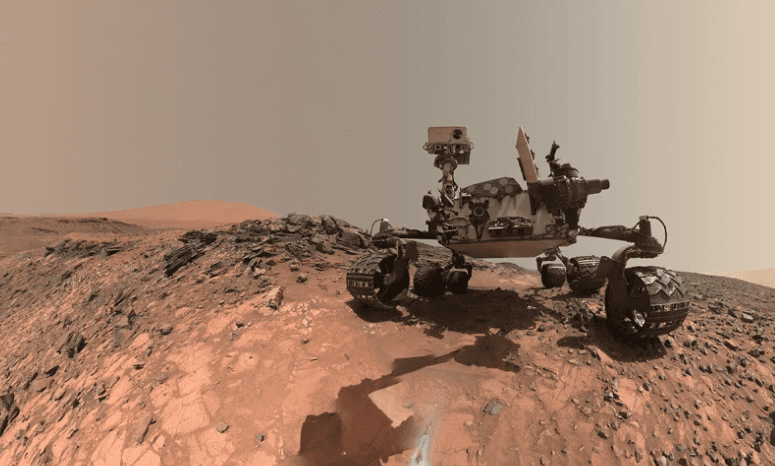
Photo Credit: NASA
4. Desert landscape
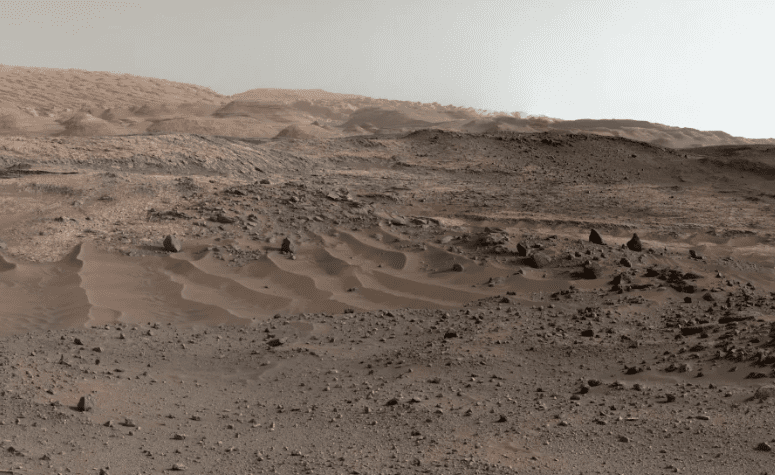

Photo Credit: NASA
5. Wide open
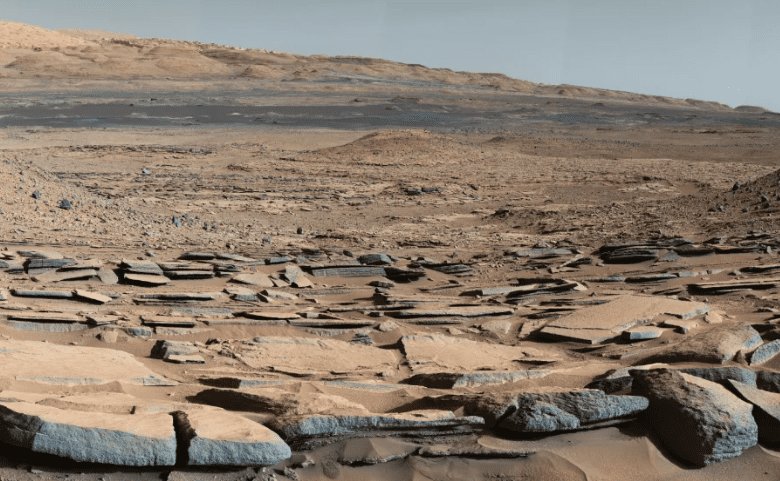

Photo Credit: NASA
6. There’s the Rover again!
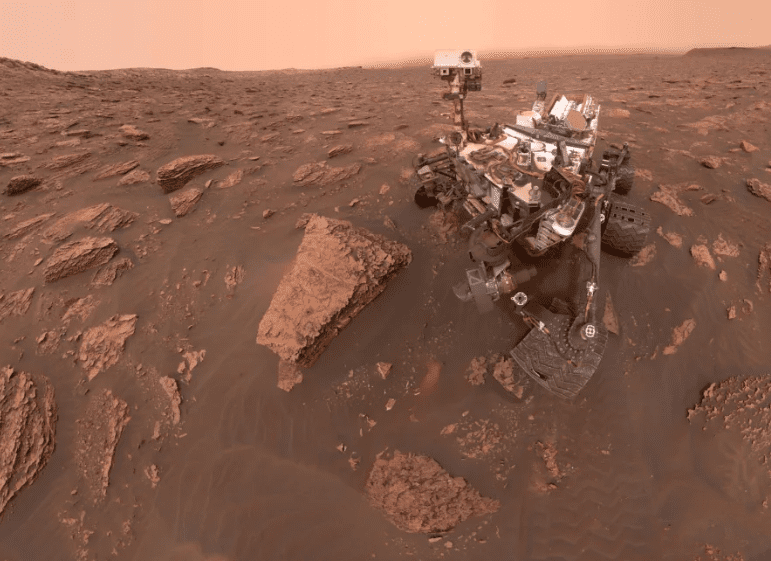

Photo Credit: NASA
7. Fish eye
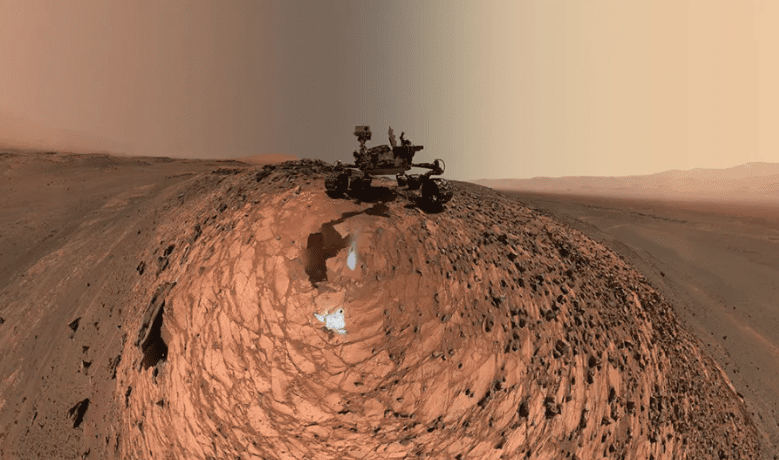

Photo Credit: NASA
8. Doing good work
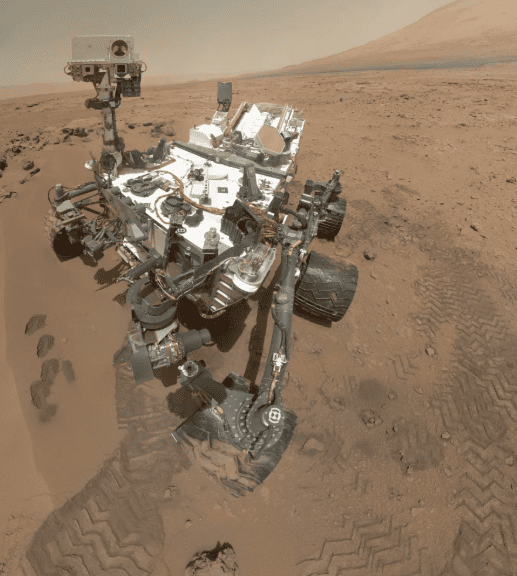

Photo Credit: NASA
9. Endless
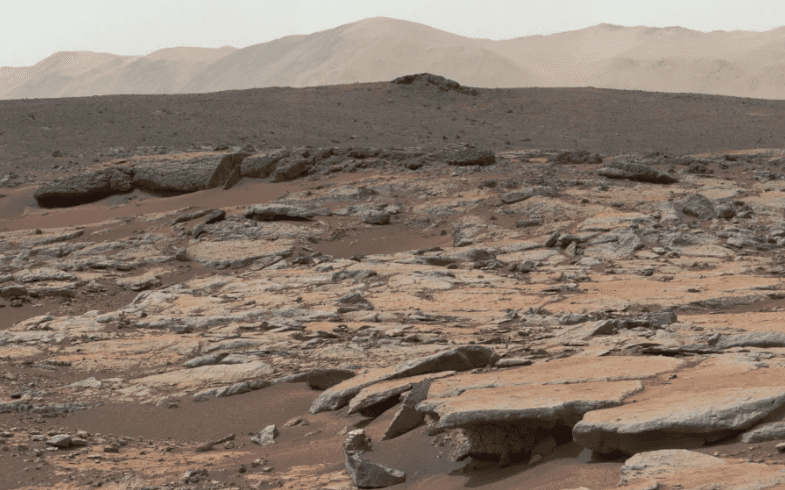

Photo Credit: NASA
10. Lonely
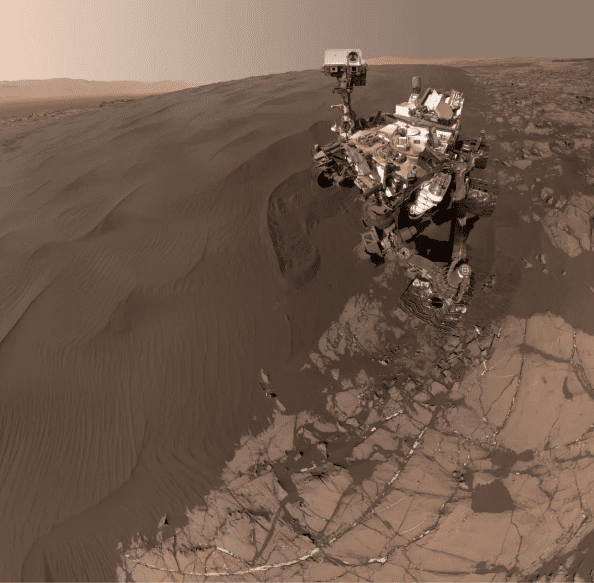

Photo Credit: NASA
11. Fascinating

Photo Credit: NASA
12. Cool shot
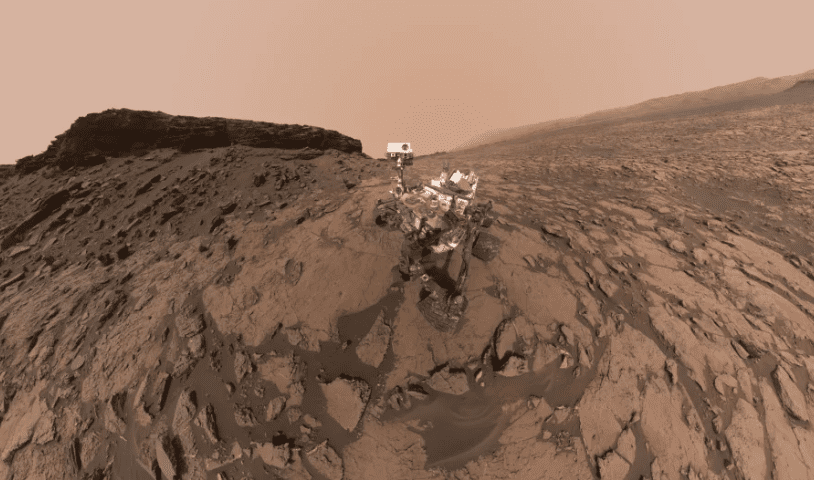

Photo Credit: NASA
13. Boulders

Photo Credit: NASA
14. Wow
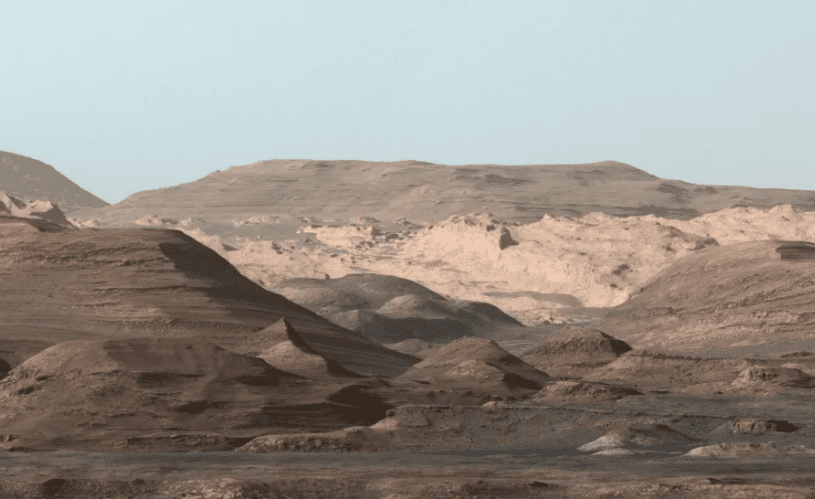

Photo Credit: NASA
15. Science rocks!
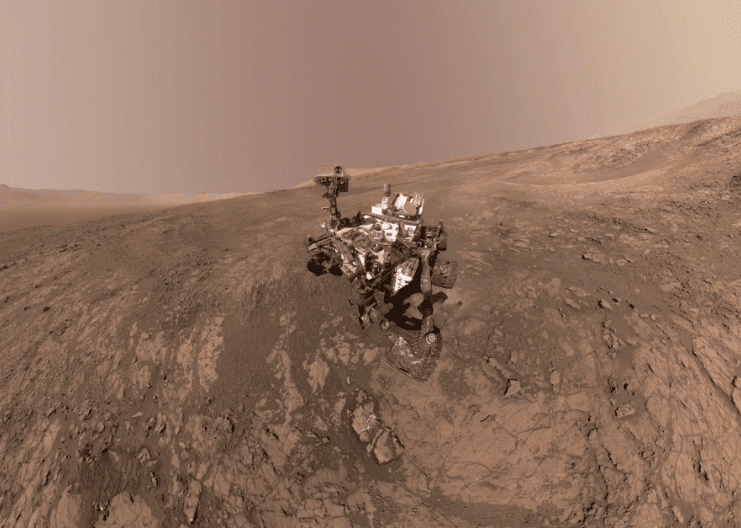

Photo Credit: NASA
Be sure to follow NASA’s progress on Mars, it gets more fascinating by the day!
The post 15 Amazing Photos of What Mars Looks Like appeared first on UberFacts.
