There have been many advancements in the past several decades that have changed and improved the way we live our lives every single day, and GPS definitely fits into that category.
Whether it’s helping us get where we’re going anywhere in the world or helping police find missing persons, to a hundred other uses in between (it’s helped me find my dog more than once), there’s no question our society is better for it.
There are two people responsible for turning the idea into a reality – one you’ve probably heard of and one you probably haven’t – and I think it’s about time they got a bit more recognition and credit, don’t you?
Image Credit: GPS.gov
GPS is short for Global Positioning System, and it means that from anywhere in the world, signals can be transmitted by a network of satellites to pinpoint your location within 3 feet. It’s right more than 95%of the time, with the most accurate of devices spotting your position within 12 inches.
The first person responsible for this scientific magic is none other than Albert Einstein, whose theories of special and general relativity play an important role in the process.
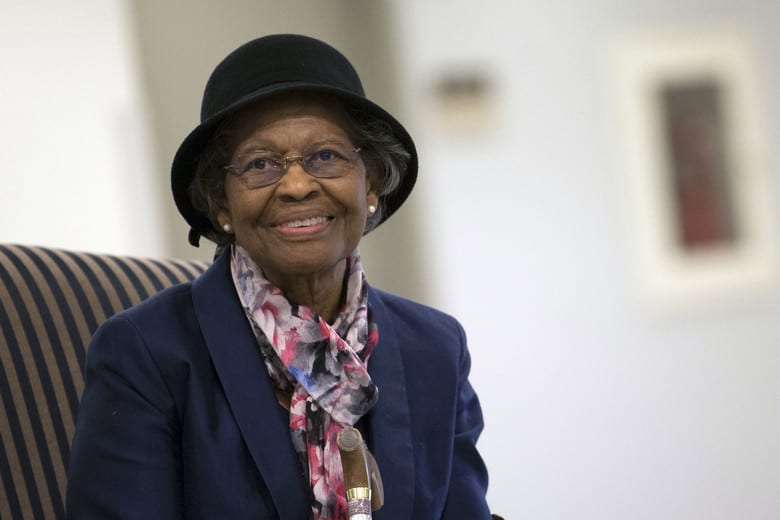
The second is a fairly obscure Black female scientists named Gladys West, whose work allows us to understand geodesy and the shape of the Earth well enough to put those physics into action.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL
Basically, you have to know three things in order to interpret signals received from the the 31 operational satellites:
- Motion: this includes the motion of both the satellites through space and the motion of the person they’re trying to pinpoint, the motion of the receiver on earth, all of which relate to the laws of Special Relativity.
- Curved Space: The gravitational blueshifting and gravitational time dilation of light as it moves between the curvature in space to the curvature on Earth’s surface, following the laws of General Relativity.
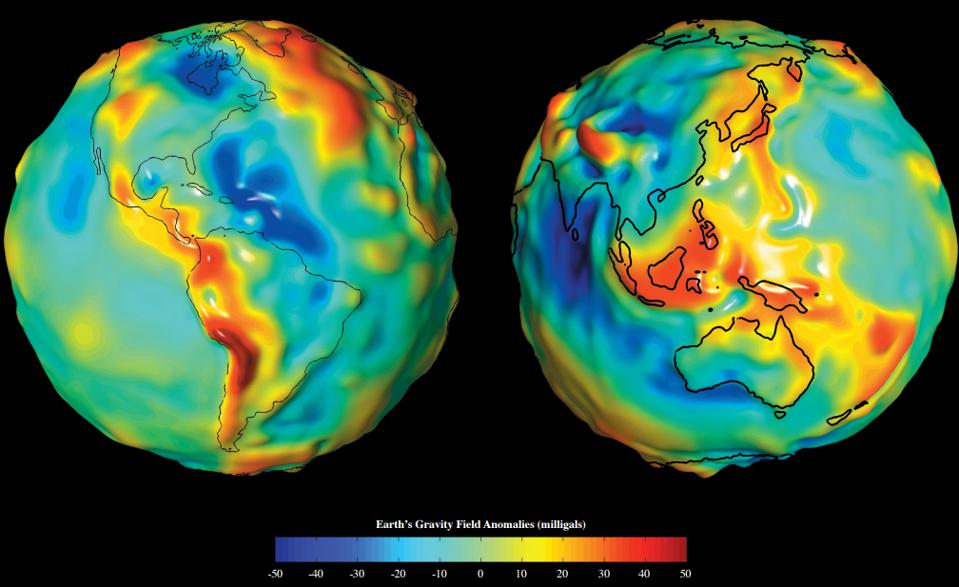
- Earth’s Gravity: It’s effects may vary by small but still substantial amounts due to mountains and valleys, the thickness of Earth’s crust, and the water present at a given location.
The rules of relativity, put forth by Einstein in the early 20th century, address all of these effects and help us mitigate them neatly.
Image Credit: NASA
Gladys West comes in with the next piece of the equation, which compensates for the fact that the Earth is not a uniform, perfect sphere with the exact same gravitational properties everywhere.
All told, the actual acceleration on Earth can be as little as 9.764 m/s² and as great as 9.834 m/s²: a difference of 0.7%.
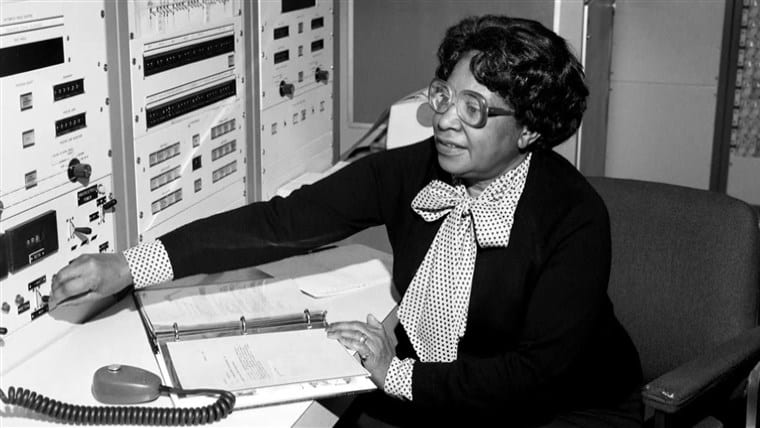
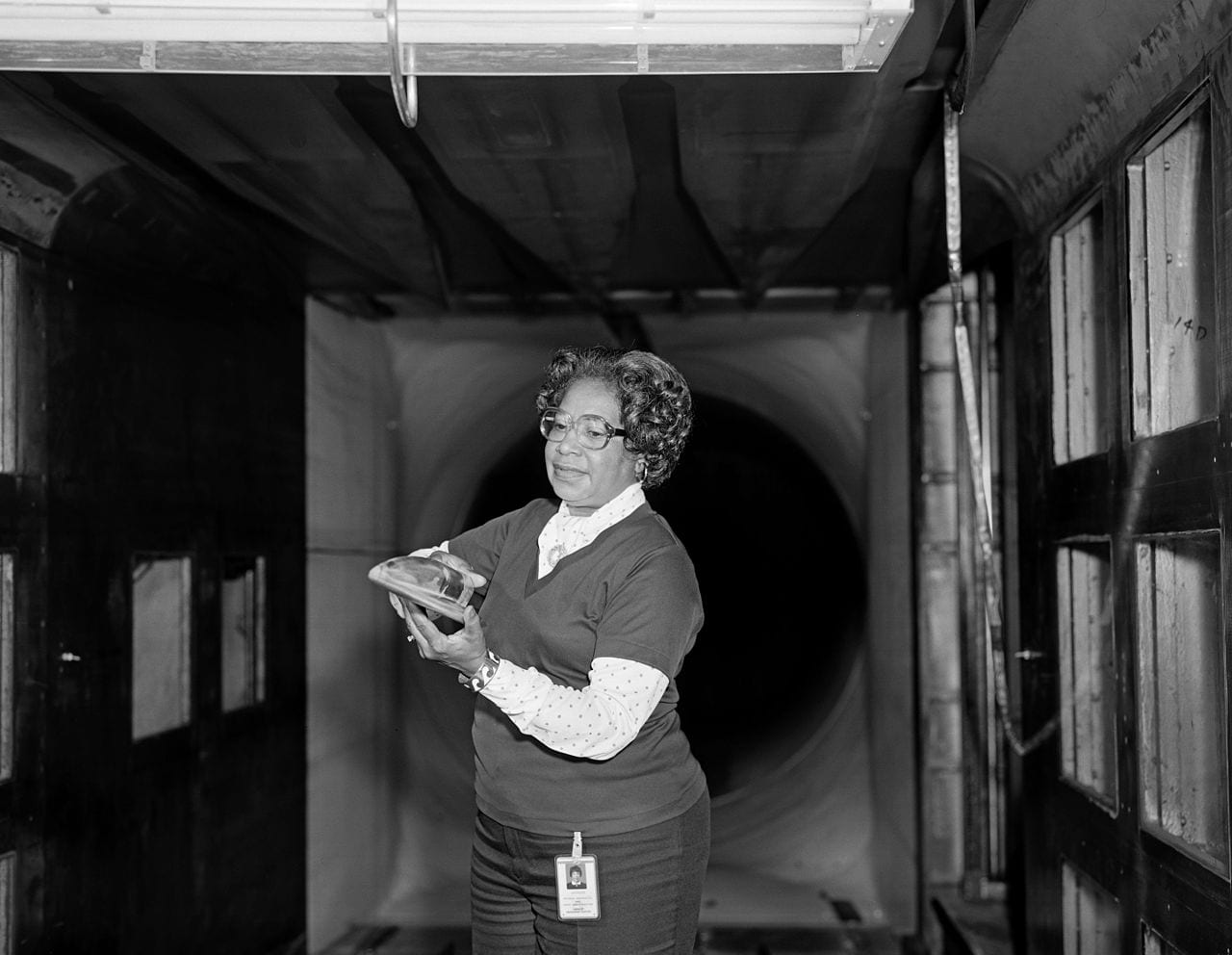
Gladys, the second Black woman ever hired as a computer programmer at the Naval Proving Ground in Virginia, specialized in large-scale computer systems and data-processing systems for the analysis of information obtained from satellites.
Image Credit: US Air Force
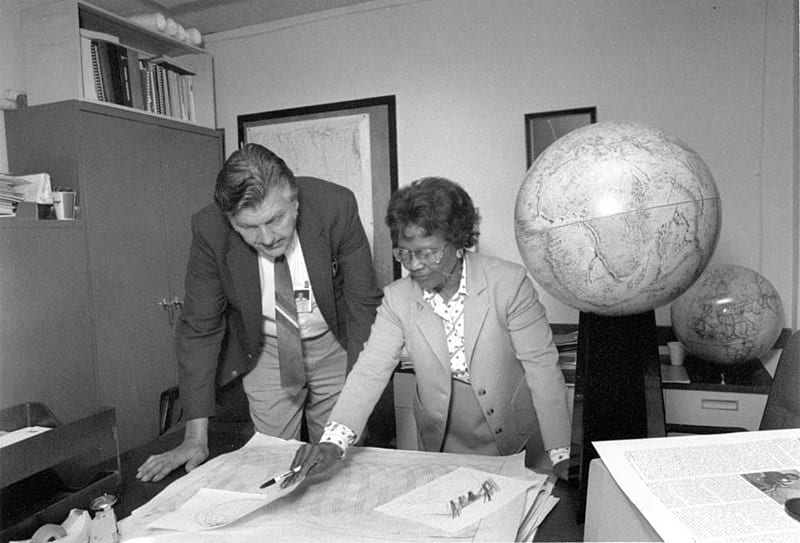
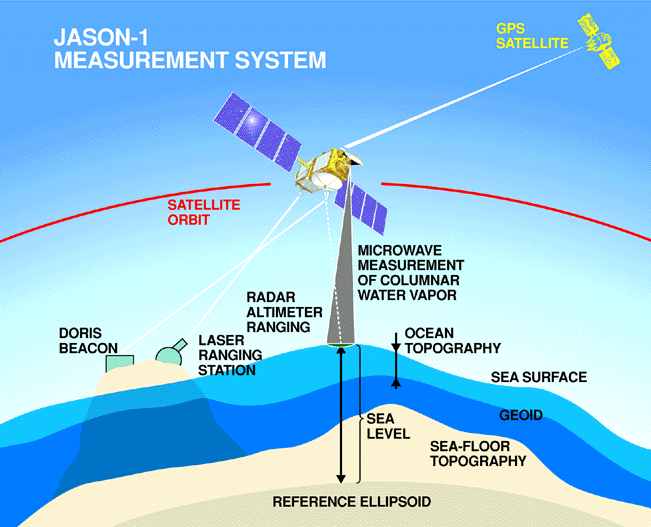
From there, she put together altimeter models of Earth’s shape in the 1960s, and served as the project manager for Seasat, the first satellite to perform remote sensing of Earth’s oceans.
Through her work, she cut the processing time for these remote sensing applications in half.
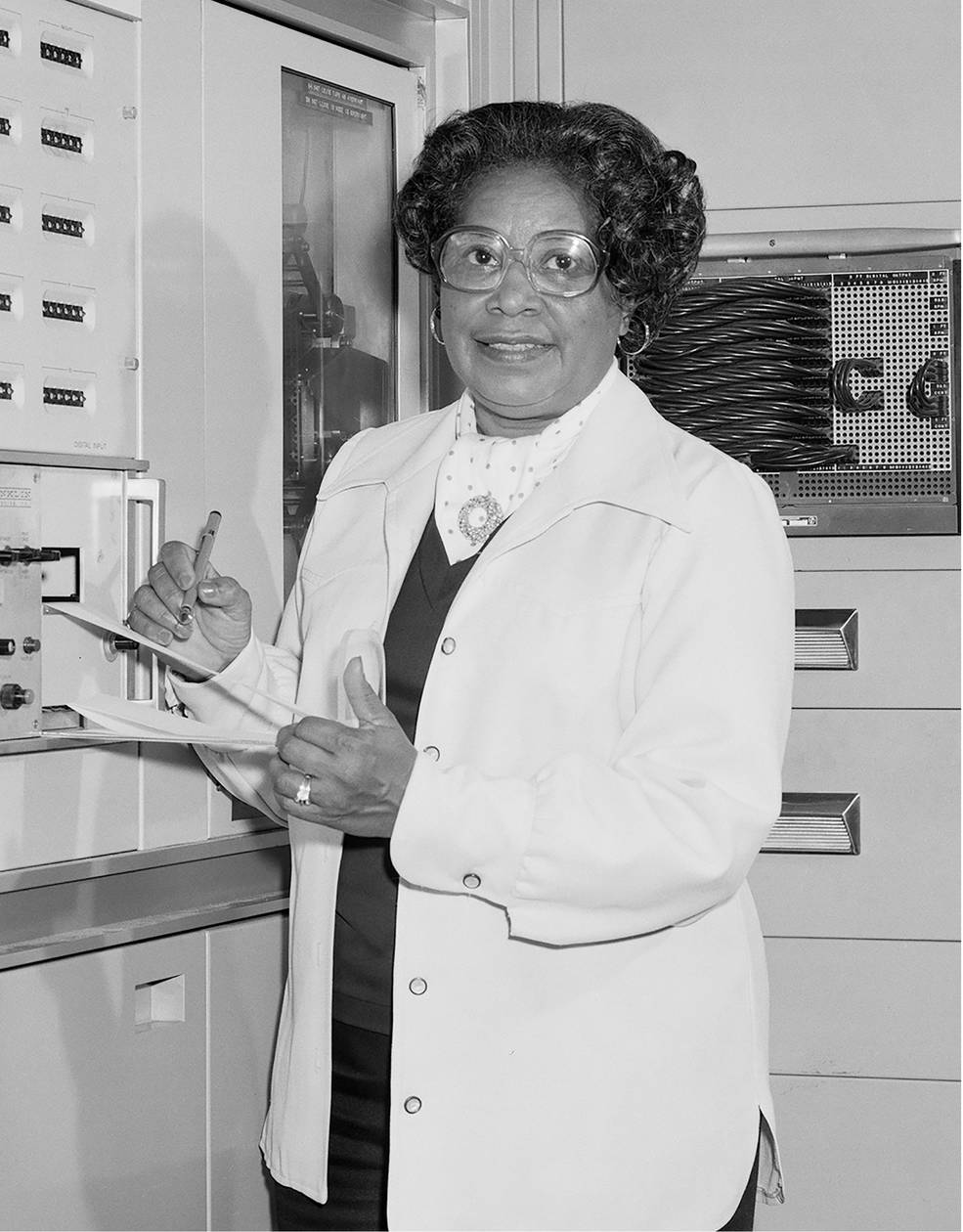
Her most revolutionary work, though, was when she programmed the computer that calculated Earth’s geoid to the kind of sufficient precisions that enabled the existence of GPS. To accomplish this, she had to account for every variation in all the forces and effects that can distort the shape of the Earth.
She wrote a guide on radar altimeter satellites, which taught others how to increase the precision of satellite geodesy with her improved technology.
Gladys was inducted into the Air Force Hall of Fame for her efforts, and is universally recognized as one of the Hidden Figures whose work with vital computations allowed the U.S. Military and NASA to complete successful missions before the advent of computing that could take over the tasks.
Image Credit: US Navy
Her commanding officer, Captain Godfrey Weekes, had this to say about his famous employee:
“She rose through the ranks, worked on the satellite geodesy, and contributed to the accuracy of GPS and the measurement of satellite data. As Gladys West started her career as a mathematician at Dahlgren in 1956, she likely had no idea that her work would impact the world for decades to come.”
For West’s part, she still uses a paper map when she travels.
Better safe than sorry, I suppose.
The rest of us, though, say thank you – especially the generations who have never seen a paper map in their lives.
The post Learn About the Two People Who Made GPS a Reality appeared first on UberFacts.